simplify-the-function-𝒇-𝒂-𝒃-𝒄-𝒅-∑𝒎-𝟐-𝟑-𝟒-𝟓-𝟏𝟑-
Quine McCluskey Minimization Technique || Example 1 | Tabulation Method | DLD | Digital ElectronicsПодробнее

Karnaugh Map with Don't Cares || Don't Care Condition in K - Map Part 1Подробнее

Simplify the following Boolean functions using K-mapПодробнее

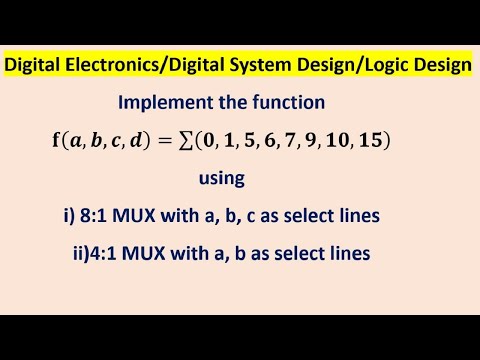
Implement the function 𝐟(𝒂,𝒃,𝒄,𝒅)=∑(𝟎,𝟏,𝟓,𝟔,𝟕,𝟗,𝟏𝟎,𝟏𝟓) using8:1 MUXПодробнее
Simplify using Quine McClusky (QM) method and realize the function using a basic gatesПодробнее

Using K map method, obtain minimal SOP expression and implement the function using NAND gates.Подробнее

Simplify the Boolean function using K map f(𝒘,𝒙,𝒚,𝒛)=∑𝝅𝑴(𝟏,𝟒,𝟓,𝟏𝟏,𝟏𝟐,𝟏𝟑,𝟏𝟒,𝟏𝟓).𝒅(𝟑,𝟗,𝟏𝟎)Подробнее

Simplify the function 𝒇(𝒂,𝒃,𝒄,𝒅)=∑𝝅𝑴(𝟎,𝟒,𝟓,𝟕,𝟖,𝟗,𝟏𝟏,𝟏𝟐,𝟏𝟑,𝟏𝟓) Using Karnaugh mapПодробнее

Simplify the function 𝒇(𝒂,𝒃,𝒄,𝒅)=∑𝒎(𝟐,𝟑,𝟒,𝟓,𝟏𝟑,𝟏𝟓)+𝒅𝒄(𝟖,𝟗,𝟏𝟎,𝟏𝟏) Using Karnaugh mapПодробнее

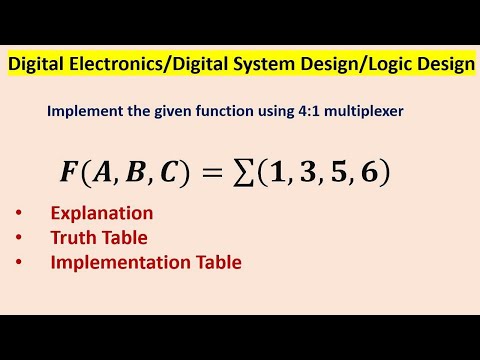
Implement the given function using 4:1 multiplexer. 𝑭(𝑨,𝑩,𝑪)=∑(𝟏,𝟑,𝟓,𝟔)Подробнее
Make a K-map for the function, f(A,B,C,D) = ¶M (3,4,5,7,11,13,15)) + d(6,8,10,12)Подробнее

Minimize four-variable logic function using K-Map, f(A,B,C,D) = ∑m(1,2,6,7,8,13,14,15) + d(3,5,12).Подробнее

Minimize the four-variable logic function using K-Map, f(A,B,C,D) = ¶m (4,6,10,12,13,15).Подробнее

Minimize the four-variable logic function using K-Map, f(A,B,C,D) = ∑m(0,1,2,3,5,7,8,9,11,14).Подробнее

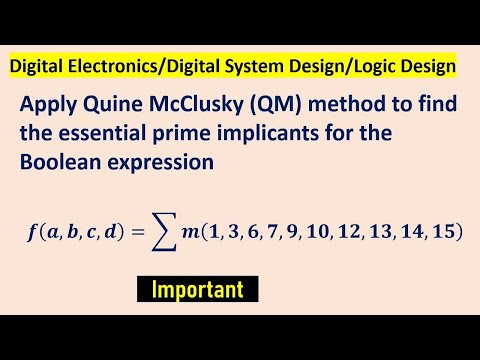
Quine McClusky (QM) method to find the essential prime implicantsПодробнее
Simply using K-map Technique. For the below expression, draw the logic diagram using AOI logic.Подробнее

Simplify given function using Quine-McCluskey Method (QM Method)Подробнее

Simplification of Boolean expressions using Kmap.Подробнее

U1L12.4 | 5 Variable K-map for SOP | Simplify the given function using K-map | K-map for SOPПодробнее

Q. 3.15: Simplify the following Boolean function F, together with the don’t-care conditions d, andПодробнее
